The following SCA methods can be handled using Token.io's API:
The Redirect authentication - the TPP redirects users to the bank interface for authentication.
Other authentication methods where additional credential information is required:
Embedded authentication - users authenticate using the TPP's interface.
Decoupled authentication - users carry out external authorization.
See Bank selection for information on selecting banks, mandatory fields and authentication models.
This section describes the API AIS integration where the TPP owns the full user experience.
See the Token.io API reference for details of the following endpoints:
GET /banksPOST /token-requestGET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/resultPOST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorizationGET /accountsGET /accounts/{accountId}GET /account-balanceGET /accounts/{accountId}/balanceGET /accounts/{accountId}/standing-ordersGET /accounts/{accountId}/standing-orders/{standingOrderId}GET /accounts/{accountId}/transactionsGET /accounts/{accountId}/transaction/{transactionId}GET /tokens/{tokenId}
Use our Launchpad to test them.
The image below is a simplified swim lane diagram of the integration flow.
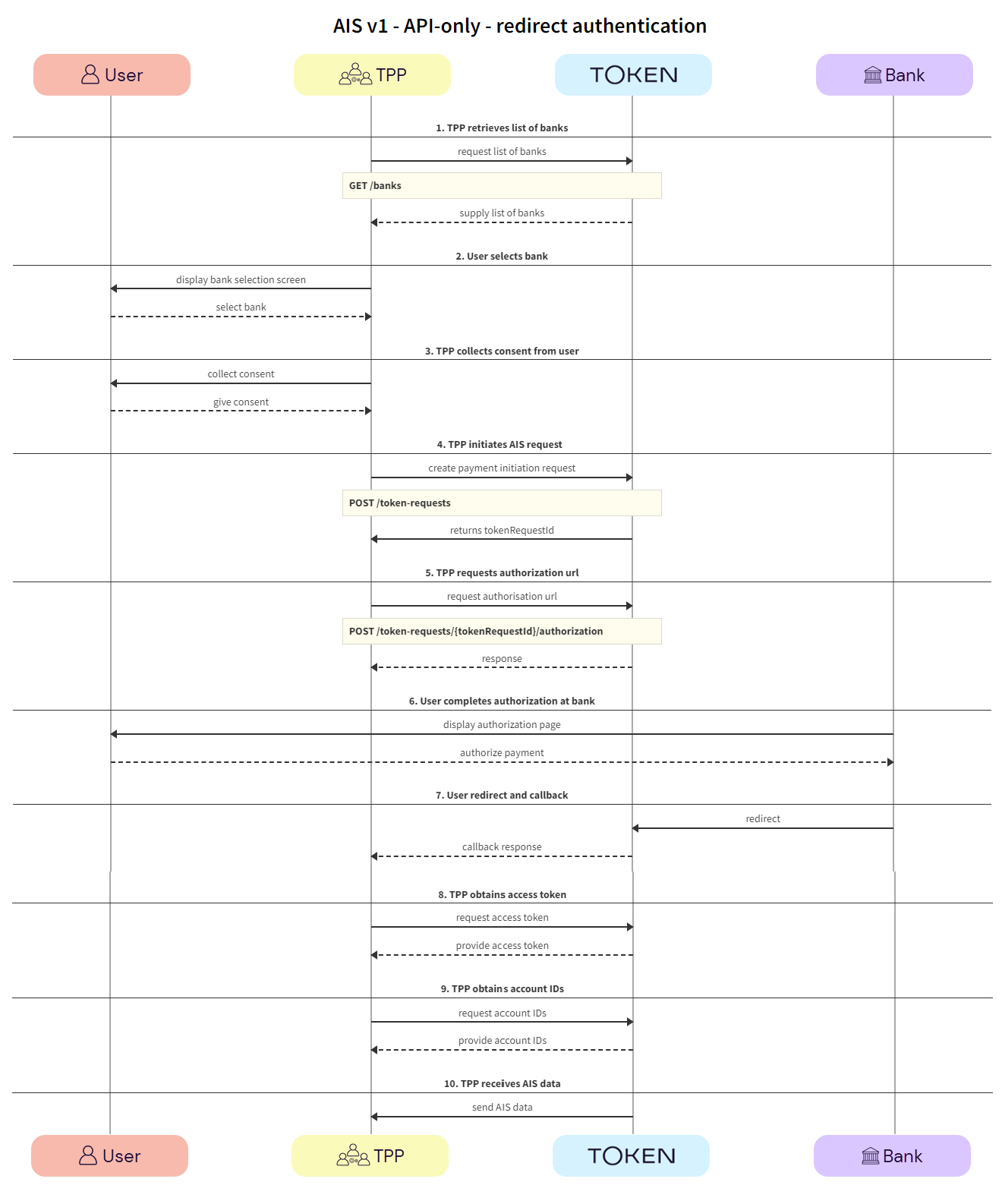
Details of the steps within the integration flow are shown below.
TPPs retrieve the list of available banks using the GET /banks call.
We recommend that this step is performed once daily, outside any AIS request, e.g., at 11pm UTC, and that the result is cached.
In the GET /banks request, there are numerous filtering criteria you can add as parameters to narrow your query. As a minimum, you should filter by your member ID.
See Mandatory fields for information on which fields must be provided for a given bank to accept an AIS request.
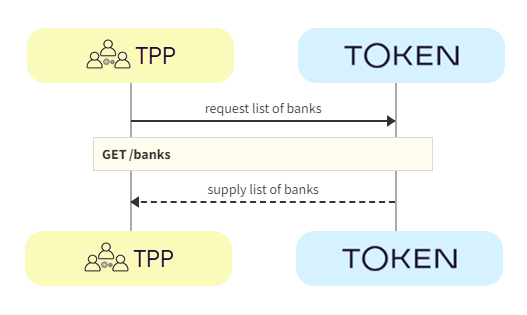
a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP requests the list of banks from Token.io.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io supplies the list of banks to the TPP.
The user selects the bank.
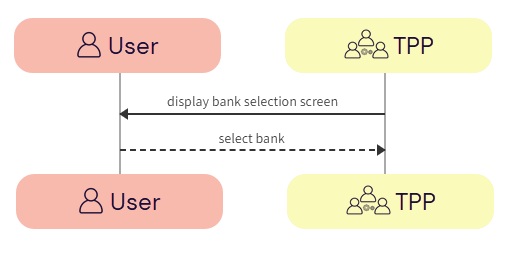
a. TPP -> User - The TPP displays the bank selection screen.
b. User -> TPP - The user selects the bank.
The TPP collects consent from the user. For more information, see User consent collection.
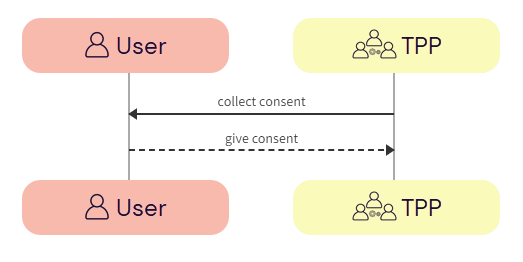
a. TPP -> User - The TPP initiates consent acceptance from the user.
b. User -> TPP - The user gives consent to the TPP.
The TPP initiates the token request with Token.io using the POST /token-requests call. Token.io responds by acknowledging the details of the request.
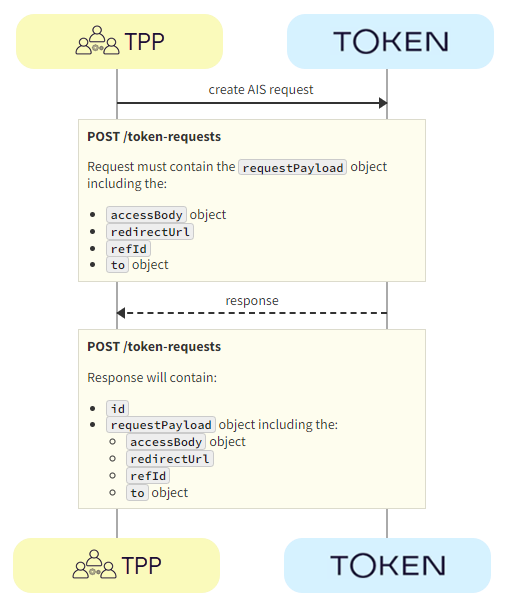
a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP creates the token request using the POST /token-requests call.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io generates a response to the token request.
The TPP requests authorization using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call. Token.io responds with the authorization URL.
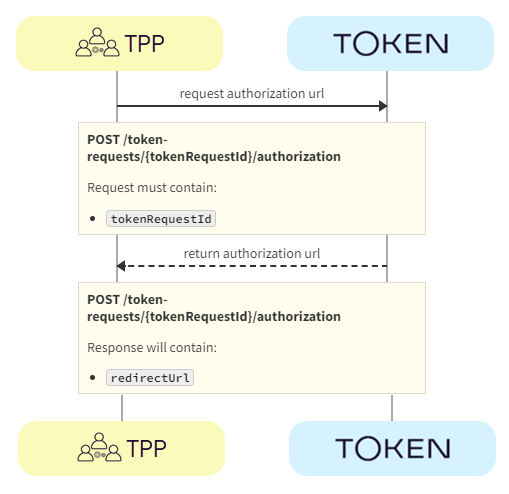
a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP requests the bank authorization URL using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io returns the redirectUrl provided by the bank.
The user completes authorization with the bank.
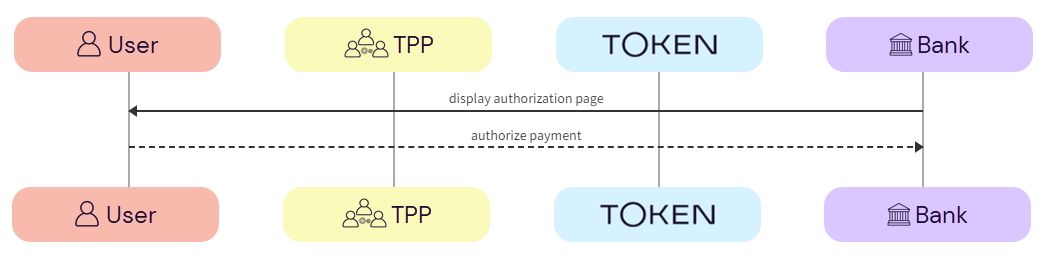
a. Bank -> User - The bank displays the authorization page to the user.
b. User -> Bank - The user authorizes the AIS request with the bank.
The user is redirected and the TPP consumes the Token.io callback response.
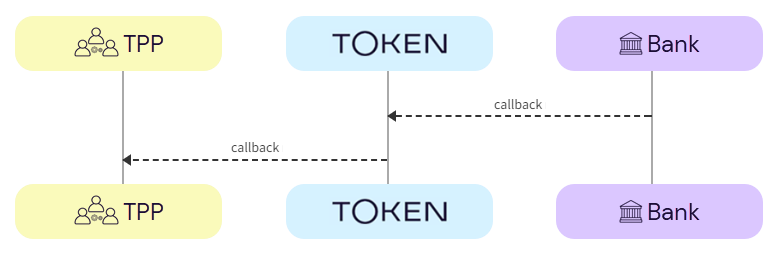
a. Bank -> Token.io - The bank redirects the user to Token.io.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io immediately redirects the user to the redirect URL provided by the TPP in the redirect URL parameter of the token-request call. The TPP then consumes the callback from Token.io.
In the API-only integration with redirect authentication and TPP callback, only the request-id is returned in the callback response.
Refer to Callback response for API-only integration for more details.
The TPP calls GET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/result to obtain the access token.
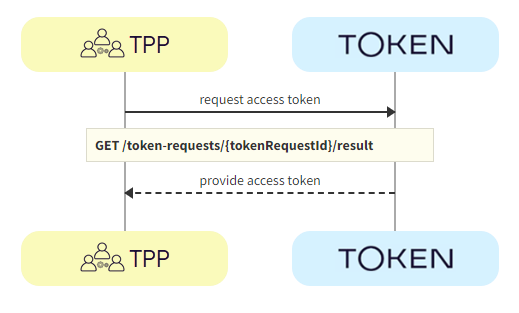
a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP calls Token.io using GET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/result to obtain the access token.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io responds with details of the access token.
The TPP calls GET /tokens/{tokenId} using the access token ID obtained in the previous step. The response contains the account IDs used for calls to the endpoints in the next step.
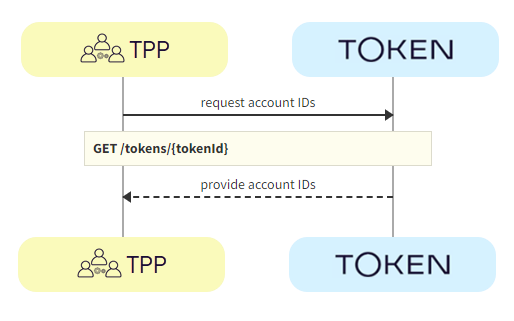
a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP calls Token.io using GET /tokens/{tokenId} to obtain the account IDs to use to retrieve the AIS data.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io responds with details of the account IDs.
Depending on your use case, you can use one or more of the Accounts endpoints to retrieve relevant account information.
See HTTP errors for information on HTTP error status codes.
In most cases, banks will redirect users to their website or mobile app. However, there are some scenarios where the bank requires the TPP to capture the fields needed for user authentication. This experience is referred to as embedded authentication.
See the Token.io API reference for details of the following endpoints:
GET /banksPOST /token-requestGET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/resultPOST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorizationGET /accountsGET /accounts/{accountId}GET /account-balanceGET /accounts/{accountId}/balanceGET /accounts/{accountId}/standing-ordersGET /accounts/{accountId}/standing-orders/{standingOrderId}GET /accounts/{accountId}/transactionsGET /accounts/{accountId}/transaction/{transactionId}GET /tokens/{tokenId}
Use our Launchpad to test them.
The image below is a simplified swim lane diagram of the integration flow.
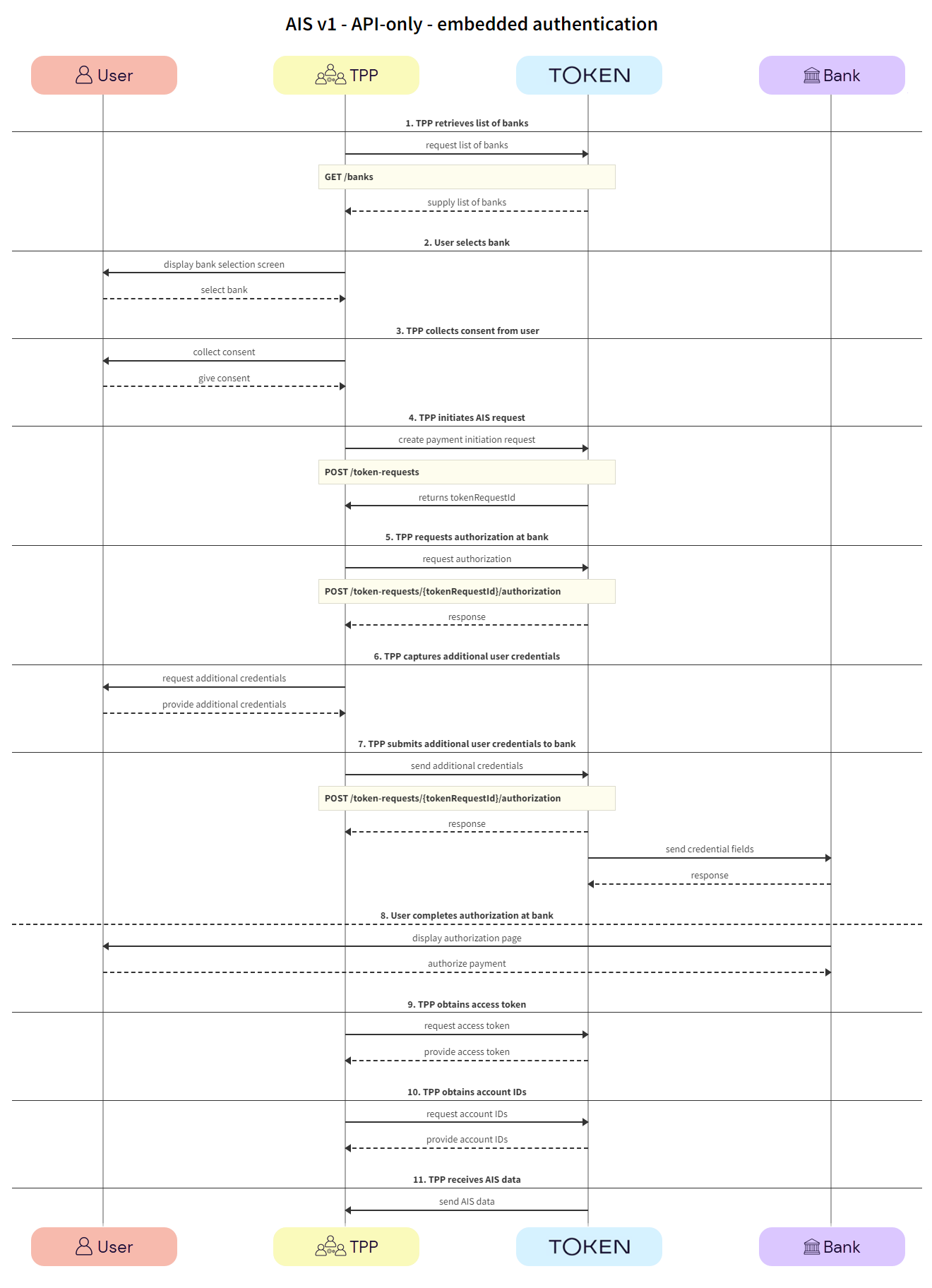
Details of the steps within the integration flow are shown below.
The TPP retrieves the list of available banks using the GET /banks call.
We recommend that this step is performed once daily, outside any AIS request, e.g., at 11pm UTC, and that the result is cached.
In the GET /banks request, there are numerous filtering criteria you can add as parameters to narrow your query. As a minimum, you should filter by your member ID.
See Mandatory fields for information on which fields must be provided for a given bank to accept an AIS request.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP requests the list of banks from Token.io.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io supplies the list of banks to the TPP.
The user selects the bank.

a. TPP -> User - The TPP displays the bank selection screen.
b. User -> TPP - The user selects the bank.
The TPP collects consent from the user. For more information see User consent collection.

a. TPP -> User - The TPP initiates consent acceptance from the user.
b. User -> TPP - The user gives consent to the TPP.
The TPP initiates the token request with Token.io using the POST /token-requests call. Token.io responds by acknowledging the details of the request.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP creates the token request using the POST /token-requests call.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io generates a response to the token request.
The TPP requests authorization using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call. Token.io responds with the fields object, containing the initial fields required for the embedded flow.
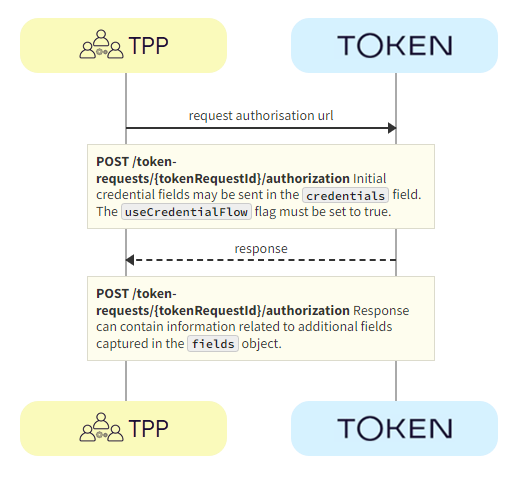
a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP requests the authorization URL using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call.
Initial credentialFields from the response to GET /banks may be sent in the credentials field. The useCredentialFlow flag must be set to true. When this flag is set to true, the credential flow is triggered. The credentials map must be populated if required by the bank (see credentialFields in the response to GET /banks), otherwise empty credentials are used.
The useCredentialFlow field should not be confused with useWebAppCredentialsFlow.
When useWebAppCredentialsFlow is set to true and the bank's flow includes embedded steps, these steps are handled by Token.io's HP, rather than by the customer's own pages.
See the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization request for more details.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io returns the fields to be used in the embedded flow. The response can contain information relating to additional fields to be captured in the fields object.
The TPP captures additional credentials from the user.
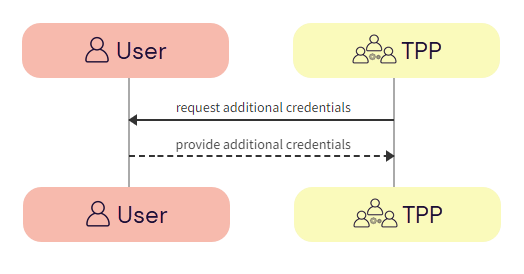
a. TPP -> User - The TPP requests additional credentials from the user.
b. User -> TPP - The user provides additional credentials to the TPP.
Using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call, the TPP submits the additional credentials to the bank via Token.io.
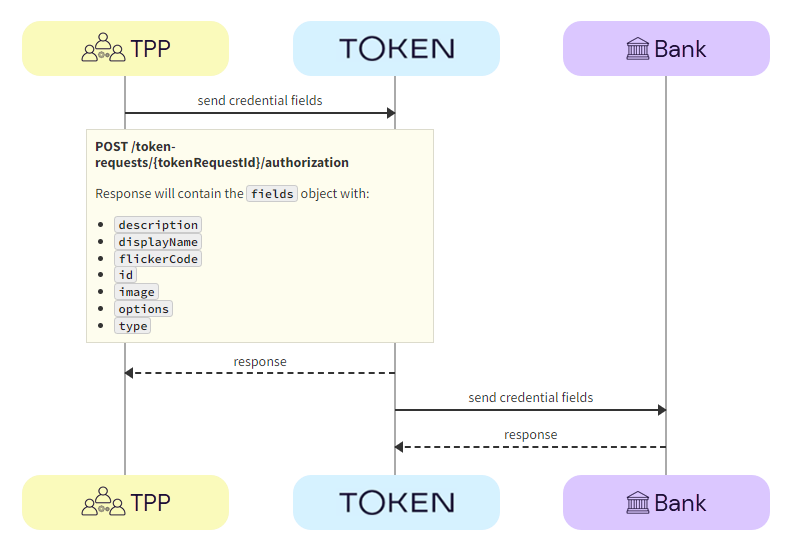
a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP sends additional credentials using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io acknowledges receipt of the additional credentials and requests more, if required.
c. Token.io -> Bank - Token.io sends this additional information to the bank.
d. Bank -> Token.io - The bank confirms receipt of the information from Token.io.
The user completes authorization with the bank.
This is an optional step. For some banks, the user may not be redirected to the bank page for completing authorization.
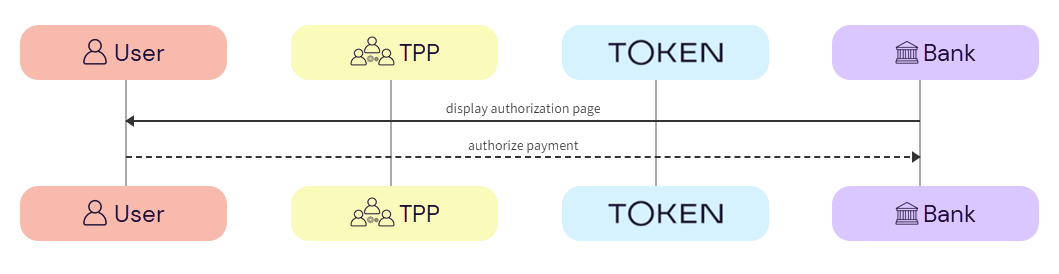
a. Bank -> User - The bank displays the authorization page to the user.
b. User -> Bank - The user authorizes the AIS request with the bank.
The TPP calls GET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/result to obtain the access token.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP calls Token.io using GET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/result to obtain the access token.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io responds with details of the access token.
The TPP calls GET /tokens/{tokenId} using the access token ID obtained in the previous step. The response contains the account IDs used for calls to the endpoints in the next step.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP calls Token.io using GET /tokens/{tokenId} to obtain the account IDs to use to retrieve the AIS data.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io responds with details of the account IDs.
Depending on your use case, you can use one or more of the Accounts endpoints to retrieve relevant account information.
See HTTP errors for information on HTTP error status codes.
With decoupled authentication, the bank carries out an additional form of authentication external to the API AIS integration. This model allows for a number of solutions, for example using a mobile phone to authenticate, or using biometrics for authentication through a separate terminal, such as a point of sale (POS) device.
See the Token.io API reference for details of the following endpoints:
GET /banksPOST /token-requestGET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/resultPOST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorizationGET /accountsGET /accounts/{accountId}GET /account-balanceGET /accounts/{accountId}/balanceGET /accounts/{accountId}/standing-ordersGET /accounts/{accountId}/standing-orders/{standingOrderId}GET /accounts/{accountId}/transactionsGET /accounts/{accountId}/transaction/{transactionId}GET /tokens/{tokenId}
The image below is a simplified swim lane diagram of the integration flow.
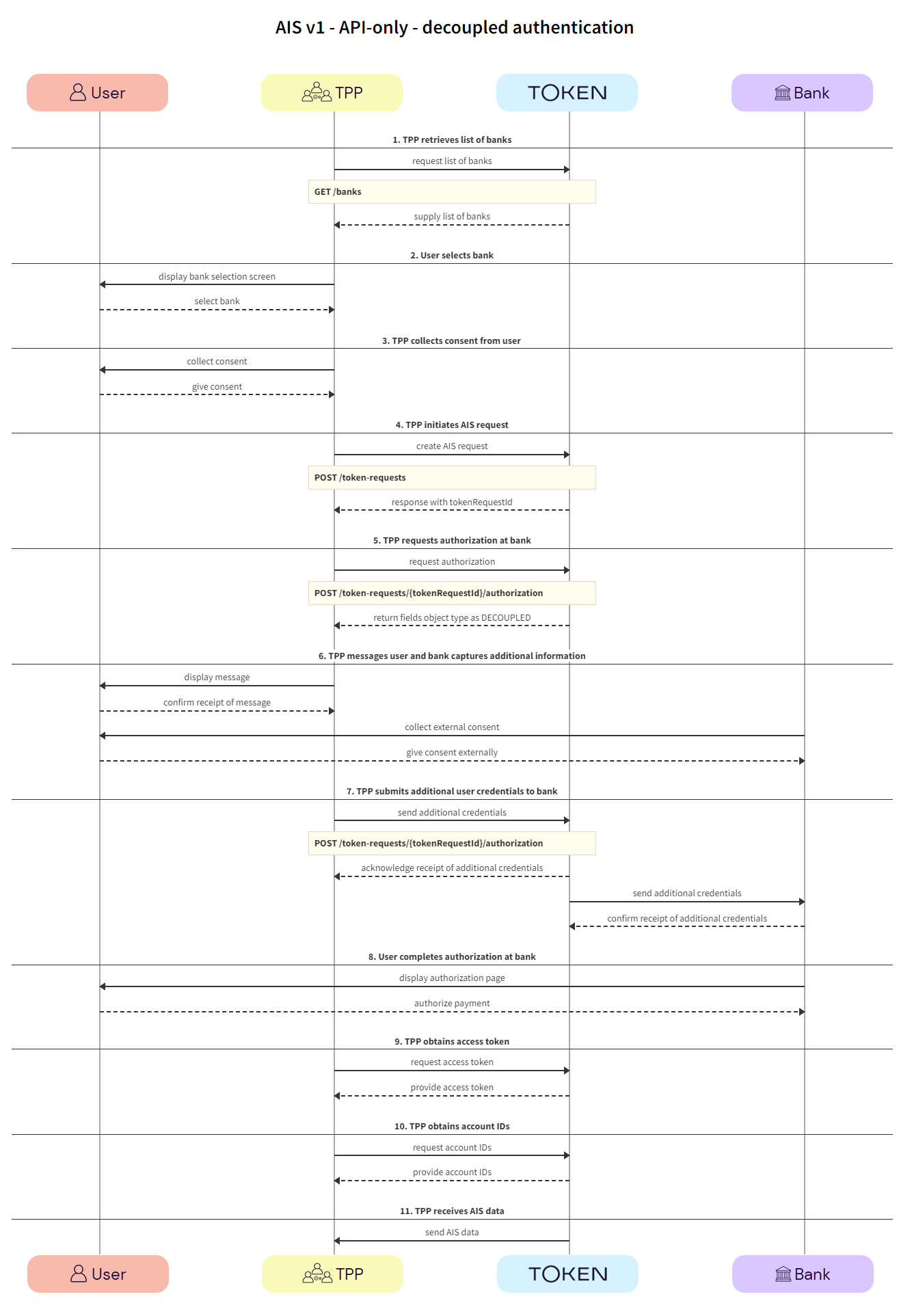
Details of the steps within the integration flow are shown below.
The TPP retrieves the list of available banks using the GET /banks call.
We recommend that this step is performed once daily, outside any AIS request, e.g., at 11pm UTC, and that the result is cached.
In the GET /banks request, there are numerous filtering criteria you can add as parameters to narrow your query. As a minimum, you should filter by your member ID.
See Mandatory fields for information on which fields must be provided for a given bank to accept an AIS request.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP requests the list of banks from Token.io.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io supplies the list of banks to the TPP.
The user selects the bank.

a. TPP -> User - The TPP displays the bank selection screen.
b. User -> TPP - The user selects the bank.
The TPP collects consent from the user. For more information see User consent collection.

a. TPP -> User - The TPP initiates consent acceptance from the user.
b. User -> TPP - The user gives consent to the TPP.
The TPP initiates the token request with Token.io using the POST /token-requests call. Token.io responds by acknowledging the details of the request.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP creates the token request using the POST /token-requests call.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io generates a response to the token request.
The TPP requests authorization using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call. Token.io responds with the fields object, containing the initial fields. In the fields object the type is returned as DECOUPLED.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP requests the authorization URL using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call.
Initial credentialFields from the response to GET /banks may be sent in the credentials field. The useCredentialFlow flag must be set to true. When this flag is set to true, the credential flow is triggered. The credentials map must be populated if required by the bank (see credentialFields in the response to GET /banks), otherwise empty credentials are used.
The useCredentialFlow field should not be confused with useWebAppCredentialsFlow.
When useWebAppCredentialsFlow is set to true and the bank's flow includes embedded steps, these steps are handled by Token.io's HP, rather than by the customer's own pages.
See the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization request for more details.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io returns the fields object with type set to DECOUPLED and the message to be displayed to the user.
See Decoupled callback response for more information on the TPP callback response.
The TPP is expected to show the message to the user and to wait for confirmation of receipt before proceeding to the next step.
The bank will then challenge the user to authenticate themselves outside the API AIS request flow. This could be in the form of an SMS to the user’s registered phone number with the bank, or biometrics through a POS device.
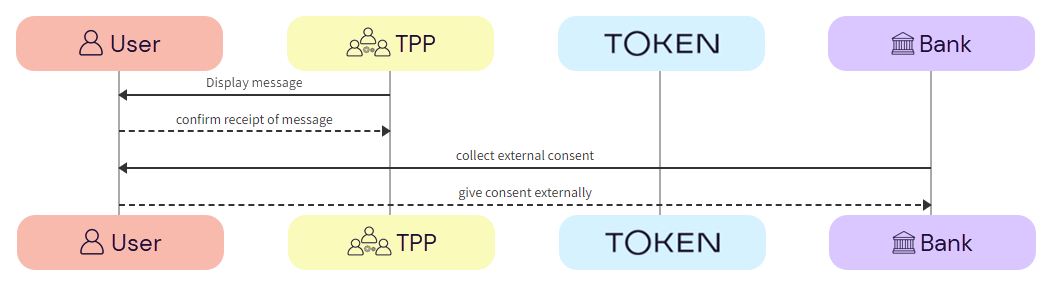
a. TPP -> User - The TPP displays the message to the user.
b. User -> TPP - The user confirms receipt of the message.
c. Bank -> User - The bank requests additional authentication from the user, through an external source, e.g., SMS. POS.
d. User -> Bank - The user provides additional authentication credentials to the bank via an external source.
Using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call, the TPP submits the additional credentials to the bank via Token.io.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP sends additional credentials using the POST /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/authorization call.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io acknowledges receipts of the additional credentials and requests more, if required.
c. Token.io -> Bank - Token.io sends this additional information to the bank.
d. Bank -> Token.io - The bank confirms receipt of the information from Token.io.
The user completes authorization with the bank.

a. Bank -> User - The bank displays the authorization page to the user.
b. User -> Bank - The user authorizes the AIS request with the bank.
The TPP calls GET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/result to obtain the access token.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP calls Token.io using GET /token-requests/{tokenRequestId}/result to obtain the access token.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io responds with details of the access token.
The TPP calls GET /tokens/{tokenId} using the access token ID obtained in the previous step. The response contains the account IDs used for calls to the endpoints in the next step.

a. TPP -> Token.io - The TPP calls Token.io using GET /tokens/{tokenId} to obtain the account IDs to use to retrieve the AIS data.
b. Token.io -> TPP - Token.io responds with details of the account IDs.
Depending on your use case, you can use one or more of the Accounts endpoints to retrieve relevant account information.
See HTTP errors for information on HTTP error status codes.
If you have any feedback about the developer documentation, please contact devdocs@token.io